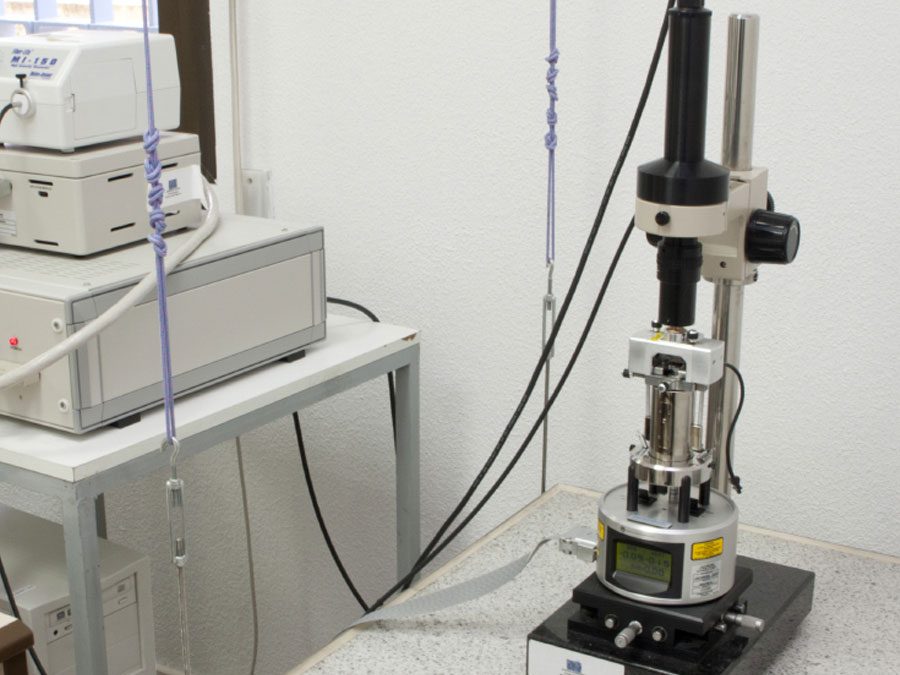
Multimode V and Multimode VIII
Scanning Probe Microscopies are key enabling techniques in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, supporting a wide range of multidisciplinary activities. The LMA hosts various multipurpose AFM/STM heads that cover a broad range of applications under near ambient conditions. Our facility houses two Multimode AFMs from Bruker (originally fabricated by Veeco and then absorbed by Bruker). Both a Multimode V and a Multimode VIII offer high-quality imaging in contact and dynamic modes. The instruments are mounted on vibration isolation damping tables allowing the operation at very low noises. The samples surface can be held in ambient conditions, in well-defined gaseous atmospheres as well as be immersed in liquid (using a liquid-cell.). Sample temperature can be varied in a range of –22 to 200 °C
Key Features
- Highest environmental control;
- remarkable variety of AFM modes;
- PeakForce™ (Multimode VIII) and HarmoniX™ (Multimode V) for efficient quantitative nanomechanical characterization”;
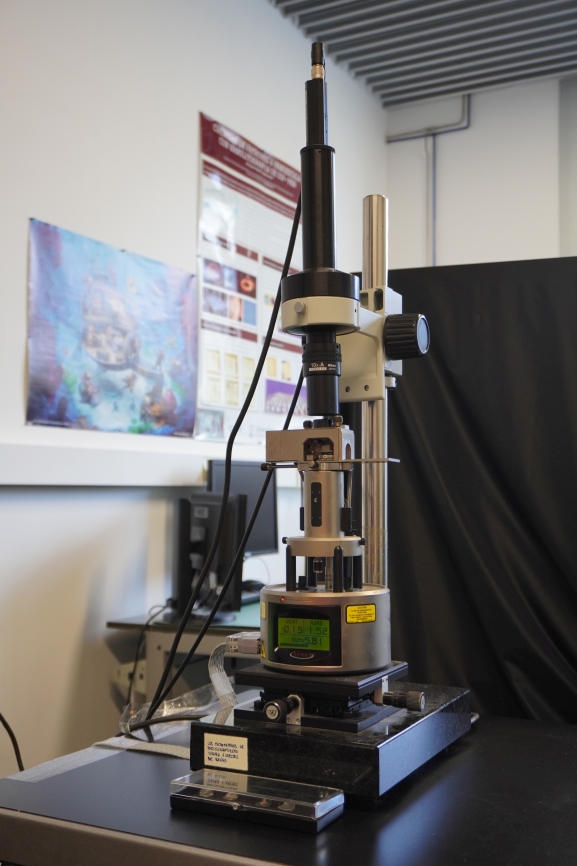
Veeko Multimode VIII

Veeko Multimode V
- What kind of information can be obtained with these instruments?
- Sample requirements
- Technical Specifications
.The following information can be obtained with our SPM instruments:
- Surface morphology. Sample surface topography with resolution down to 2 Å.
- Quantitative Nano Mechanics (QNM Peakforce™). Quantitative local measurement of the sample’s elastic modulus, adhesion and deformation as well as the tip-sample energy dissipation on surfaces (on Multimode VIII only)
- HarmoniX™ for mechanical characterization. (Multimode V only)
- Closed-loop long-range Z-scanner (Pico Force) for force spectroscopy applied on biomolecules, complexes and cells, bacteria and virus
- Single-Molecule Force Spectroscopy for Nanomechanical studies by means of Pull‐push experiments for inter and intra- molecular force measurements, with 1 pN resolution.
- Lateral force microscopies (LFM).
- Torsional Resonance Mode (TRmode™).
- Conductive AFM (c‐AFM). Quantitative local electrical resistance measurements.
- Scanning Capacitance Microscopy (SCM)
- Scanning Spreading Resistance Microscopy (SSRM) for 2D charge carrier mapping on semiconductor surfaces
- Kelvin Force Probe Microscopy (KPFM). Qualitative measurements of local surface contact potential.
- Electric Force Microscopy (EFM) for the detection of surface charge distribution and differences in surface potential
- Magnetic Force Microscopy (MFM) for the detection of surface magnetization.
- Piezoresponse Force Microscopy (PFM, on-field only). Using the tip as electrode and surface deformation sensor.
- Electro-chemical properties (EC‐SPM). Study of chemical reactions on surfaces under controlled environments.
The sample should exhibit a lower roughness than the range of the piezo scanner.
The size of the sample should be small enough to fit inside of the microscope, around 1 cm2 in surface and 0.5 cm in thickness.
Types of samples that can be studied with the environmental SPMs include:
- Biological samples (DNA, proteins and peptides; cells, viruses and bacteria; biological tissues, etc.).
- Organic and inorganic thin films.
- Gels and Polymers.
Environment: Air, gas, liquid and electrochemical cell
Temperature range: [-25, 200] ˚C
Scanner (exchangable): type J: 125 µm(X) x 125 µm(Y) x 5 µm(Z), type E: 12 µm x 12 µm x 3 µm; PicoForce 40 µm(X) x 40 µm(Y) x 20 µm(Z)
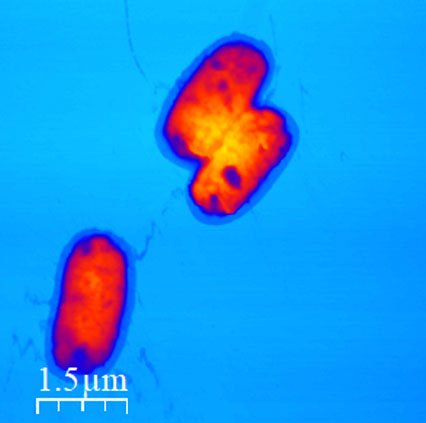

Fig 1: Air topography of Rizobacteria
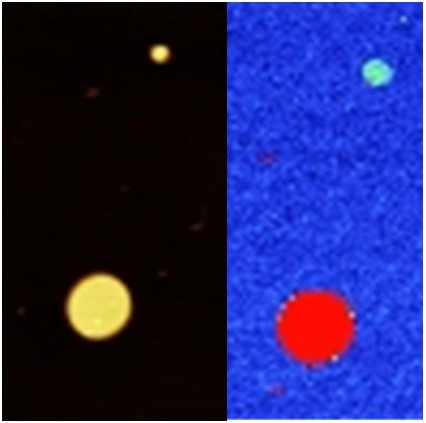
Fig 2: Graphene nanoflakes on mica
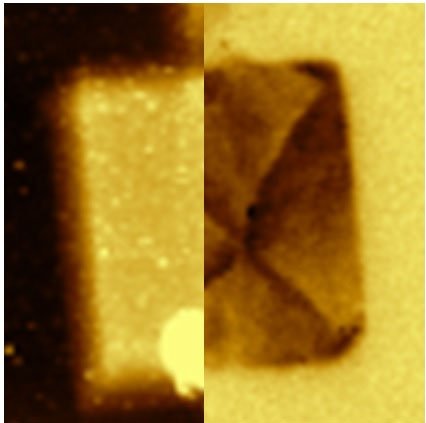
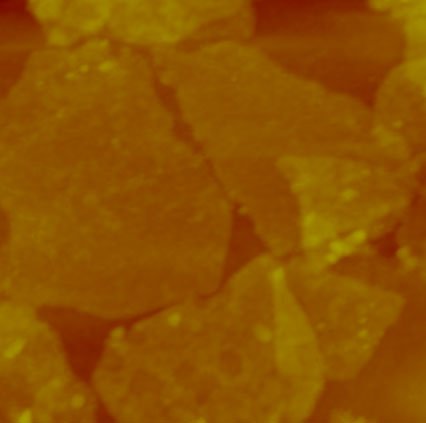
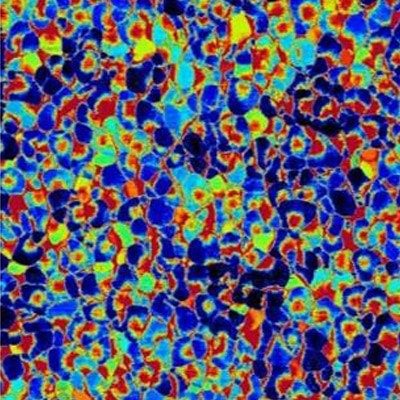
Fig 5: Stainless steel, resiscope mode, 1µm
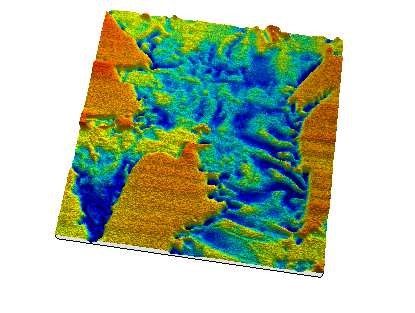
Fig 6: Stainless, MFM mode, 18µm
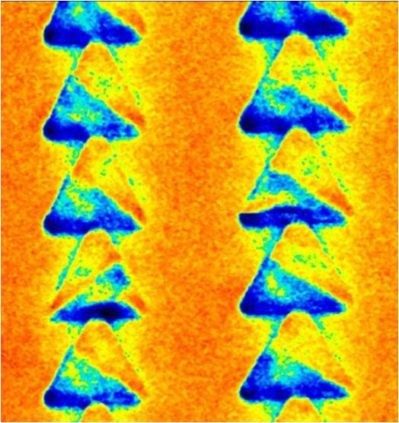
Fig 7: Magnetic triangles structures, MFM mode, 4.5µm
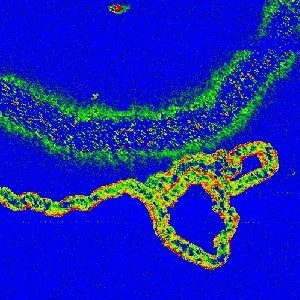
Fig 8: Nanotube on ITO, Soft ResiScope mode, 6µm
Laboratorio de Microscopías Avanzadas
We are a unique initiative at national and international levels. We provide the scientific and industrial community with the most advanced infrastructures in Nanofabrication, Local Probe and Electron Microscopies for the observation, characterization, nanopatterning and handling of materials at atomic and molecular scale.
Contact information
Campus Río Ebro, Edificio Edificio I+D+i
Direct Links
© 2021 LMA | Website developed by o10media | Política de privacidad | Aviso legal | Condiciones de uso | Política de Cookies |







